| Y-chromosome Haplogroups |
In addition to your Y-chromosome STR results, we are able to accurately predict which "haplogroup" your Y-chromosome belongs to. Haplogroups can be thought of as branches of the Y-chromosome genetic tree. With its roots in Africa approx. 140,000 years ago, as time has progressed, small mutations have occurred on the Y-chromosome. When a mutation happens (called a SNP, pronounced "snip"), the tree branches so that over time and as people have migrated into different continents and regions, we see a tree-like structure with branches found in certain parts of the world.
Because particular STR patterns are seen within particular haplogroups, on most occasions we can predict which haplogroup you are in and where your Y-chromosome fits into this Y-chromosome tree. Along with the prediction, we also provide the history, background and mapped distribution of your haplogroup.
Please be aware that, whilst our comparative database uses up to date information, it may not be possible to make an accurate prediction on all occasions and sometimes no prediction can be made.
| Your Predicted Haplogroup: R1a |
Haplogroup R1a, defined by the SNP marker SRY10831b, is part of the ancestral R1-M173 of which ancestors first arrived first arrived in Europe from West Asia during the Upper Paleolithic period (35,000-40,000 years ago). R1a is also widespread across South and Central Asia and up into Siberia. Haplogroup R1a1, defined by M17 is a major component within Haplogroup R1a. There is some suggestion that R1a and R1a1 split within Southern and Western Asia. Several possibilities for the spread of R1a and R1a1 exist, which include recent Slavic migration from the 5th century AD, movement of Kurgan people associated with the domestication of the horse and/or the re-colonization of Europe following the end of the last ice-age.
As the last ice-age began, it became necessary to move down to below the tree-line to hunt game. At its peak, the ice shelf within Europe extended down as far as southern Ireland, the middle of England and across northern Germany. Scandinavia was entirely covered. The sea-ice pack extended as far as northern Spain and tundra covered much of continental Europe. The tree-line at the height of the ice-age was as far south as Southern France, Northern Italy, north of the Balkans and across the Black Sea.
People with Haplogroup R1a Y-chromosomes retreated to below these regions where they established themselves, primarily within the region between the Black and Caspian Seas. As the ice-age ended and the fauna and flora were able to move northward again, people in R1a also migrated north and eastward. Of interest, more that 50% of Ashkenazi Levites are R1a1 whereas it is very low in other Jewish communities.
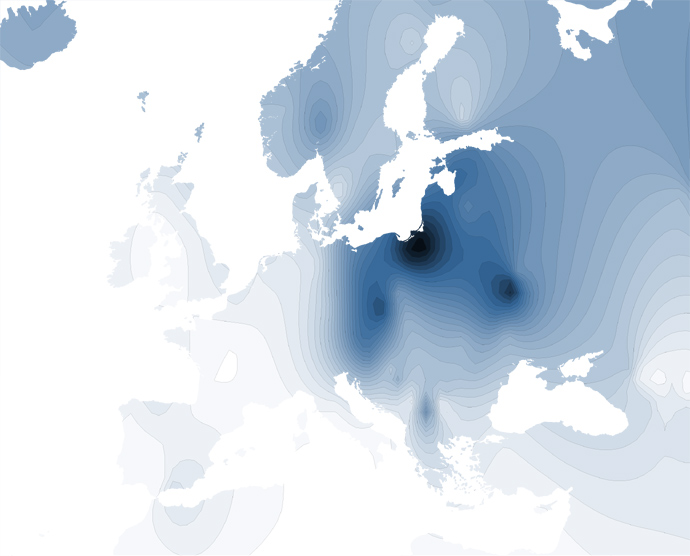
| Distribution of Haplogroup R1a |